The hock joint holds the key to unlocking your horse’s best performance. Responsible for absorbing shock, providing stability and supplying propulsion, the hock is both a powerhouse and a weak spot. It’s what enables lightning-fast runs and clean-and-tight turns, but as a large, complex and critical joint, any inflammation or injury to the hock can sideline your equine athlete.
#1 What does a horse’s hock actually do?
In the world of equine anatomy, the hock is a vital and intricate joint that plays a crucial role in a horse’s movement and overall athletic ability. Situated on the hind limb, the hock serves as the equivalent of the human ankle joint.
The hock is composed of several bones, including the tibia, fibula, talus, and calcaneus, collectively forming a complex joint capable of flexion, extension, and limited rotation. These bones are supported by an intricate network of ligaments, tendons, and muscles, providing stability and allowing for powerful propulsion during locomotion.
The hock’s primary function is to absorb and transmit the forces generated by the hind limbs during movement, particularly in activities involving jumping, turning, and pushing off the ground. The joint’s robust structure enables a horse to generate thrust, maintain balance, and execute precise movements.
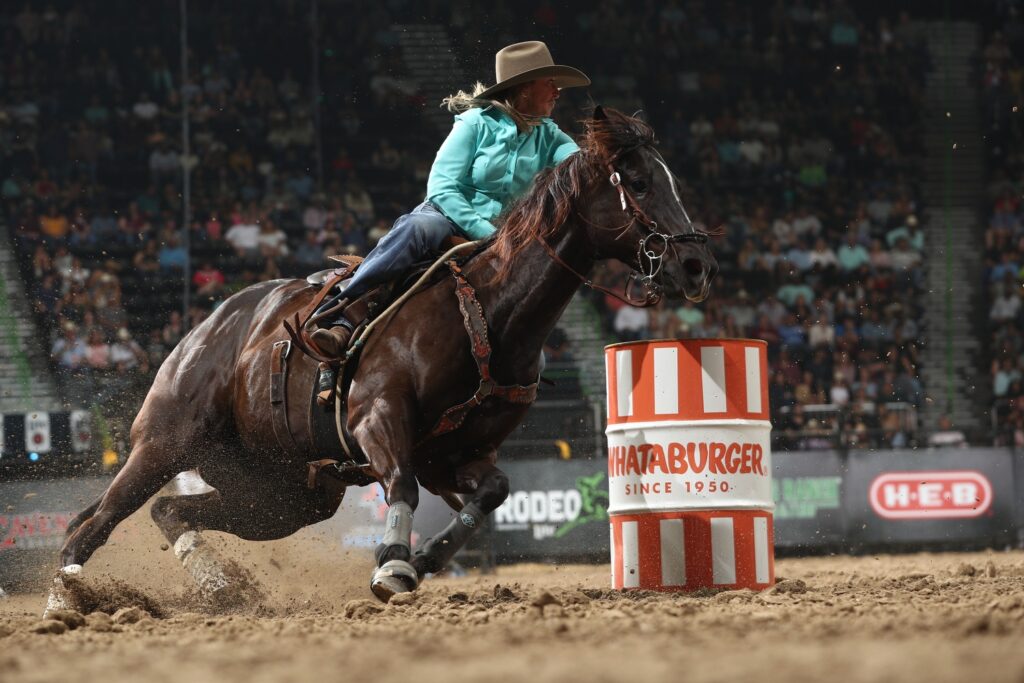

#2 Common hock issues in barrel horses
The hock joint of a horse is subjected to significant stress and strain during athletic activities, which can lead to various challenges and common issues. Understanding these challenges is crucial for horse owners, trainers, and veterinarians to identify and address potential problems promptly. Here are some common issues related to the hock:
- Hock Arthritis: Arthritis, also known as degenerative joint disease, can affect the hock joint. Over time, the cartilage lining the joint may wear away, resulting in inflammation, pain, and reduced mobility. Hock arthritis commonly occurs in older horses or those involved in repetitive and strenuous activities.
- Bone Spavin: Bone spavin refers to the formation of bony growth or osteophytes within the hock joint. This condition can result from joint instability or the body’s attempt to stabilize a weakened joint. Bone spavin causes lameness, stiffness, and swelling in the affected hock, impacting a horse’s performance.
- Soft Tissue Injuries: The soft tissues surrounding the hock, including ligaments and tendons, are susceptible to strains, tears, and overuse injuries. These injuries can occur due to sudden movements, excessive stress, or repetitive strain. Inflammation, swelling, lameness, and restricted movement are common signs of soft tissue injuries in the hock.
- Bog Spavin: Bog spavin refers to the swelling or distension of the joint capsule of the hock due to excess synovial fluid accumulation. It often occurs secondary to other hock issues, such as arthritis or soft tissue injuries. While bog spavin itself may not cause lameness, it can be a sign of an underlying problem that requires attention.
- OCD Lesions: Osteochondritis dissecans (OCD) is a condition characterized by the development of abnormal cartilage within the joint. In the hock, OCD lesions can occur in various locations, causing pain, lameness, and joint effusion. Early detection and appropriate treatment are crucial to prevent further joint damage.
- Conformation-related Issues: Poor conformation, such as sickle hocks or cow hocks, can predispose a horse to hock problems. Abnormal alignment or stress on the joint due to conformational faults can lead to increased wear and tear, instability, and a higher risk of injuries.
- EIPH and Lasix with Dr. Melissa Fenn
- Horse Health: Duct Work
- Flex On ‘Em: Understanding 7 Key Muscle Groups for Barrel Racing Horses
#3 How can I tell if my horse has hock issues?
Assessing hock issues in a barrel horse requires careful observation and, ideally, the guidance of a veterinarian or an experienced equine professional. However, here are some signs that may indicate hock issues in a barrel horse:
- Lameness: Horses with hock problems often exhibit lameness, which can manifest as an uneven gait or an unwillingness to move freely. The lameness may be more noticeable during turns or when the horse is asked to perform sudden bursts of speed.
- Swelling or heat: Observe the hock area for any signs of swelling, inflammation, or heat. These could indicate joint problems or an injury.
- Stiffness: Horses with hock issues may show stiffness, especially when starting to move after a period of rest. They might resist bending their hocks or have difficulty flexing them properly.
- Changes in performance: If your barrel horse starts to show a decline in performance, such as slower times, difficulty making tight turns, or reluctance to engage in the activity, it could be due to hock issues.
- Changes in behavior: Horses experiencing pain or discomfort in their hocks may display changes in behavior. They might become irritable, exhibit resistance or unwillingness to perform specific maneuvers, or demonstrate a decrease in overall enthusiasm for work.
It’s important to note that these signs can also be indicative of other conditions, and a proper veterinary examination is crucial for an accurate diagnosis. If you suspect your horse has hock issues, consult with a veterinarian who can perform a thorough evaluation and recommend appropriate treatment or management options.
#4 How can I prevent hock issues in my barrel horse?
- Warm-up and Cool-down Protocols: Adequate warm-up and cool-down routines are vital for maintaining the health and flexibility of a horse’s hock joint. A study conducted by Draper et al. (2017) demonstrated that a structured warm-up routine consisting of low-intensity exercises, such as walking and trotting, significantly reduced the incidence of hock injuries in performance horses. Similarly, a thorough cool-down period allows the horse’s muscles and joints to gradually return to their resting state, reducing the risk of strain and injury.
- Proper Conditioning: Regular exercise and conditioning play a crucial role in strengthening the musculoskeletal system of barrel horses, including the hock joint. A study by Morris et al. (2020) emphasized the importance of a comprehensive conditioning program that incorporates a mix of cardiovascular training, strength-building exercises, and targeted stretching. Gradual increases in exercise intensity and duration, coupled with proper rest and recovery periods, aid in the development of robust hock joint structures and reduce the likelihood of injury.
- Appropriate Footing: The type of footing on which barrel horses train and compete can impact the forces exerted on their hock joints. Research conducted by Dyson et al. (2018) highlighted that excessively hard or deep footing can increase the strain on the hocks, potentially leading to injuries. Maintaining a consistent and suitable surface, such as well-maintained sand or engineered footing, helps minimize the risk of hock-related issues.
- Regular Veterinary Evaluation: Regular veterinary examinations are essential for identifying any underlying issues in a horse’s hock joint. Studies by van Heel et al. (2019) emphasized the importance of radiographic assessments and thorough clinical evaluations to detect early signs of hock pathology. Early detection and timely intervention, such as joint injections or appropriate medical treatments, can help prevent the progression of minor issues into more significant injuries.
- Proper Tack and Equipment: The selection and use of suitable tack and equipment can contribute to hock injury prevention. A study by Clayton et al. (2017) found that ill-fitting saddles and improper bitting techniques can lead to altered movement patterns, which may place excessive stress on the hock joint. It is crucial to consult with equine professionals, such as trainers and saddle fitters, to ensure that the horse’s equipment is correctly fitted and does not impede their natural movement.
#5 Targeted treatments
When it comes to treating hock lameness and injuries in horses, several options are available. The choice of treatment depends on the specific condition and severity of the injury. It is essential to consult with a veterinarian to determine the most suitable course of action. Here are some common treatment options for horses with hock lameness and injury:
- Rest and Rehabilitation: In many cases, rest is the first step in the treatment process. Horses with hock injuries often require a period of restricted exercise to allow the affected joint to heal. Stall rest or limited turnout in a small paddock can help prevent further damage and promote the horse’s recovery. Following the rest period, a structured rehabilitation program that includes controlled exercise and physiotherapy may be recommended to gradually rebuild strength and range of motion in the hock joint.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly prescribed to manage pain and reduce inflammation associated with hock injuries. Medications such as phenylbutazone (Bute) and flunixin meglumine (Banamine) can provide temporary relief and improve the horse’s comfort level during the recovery process. However, it’s important to note that these medications do not address the underlying cause of the injury and should be used under veterinary guidance.
- Joint Injections: In cases of hock lameness caused by inflammation or osteoarthritis, joint injections may be recommended. These injections typically involve the administration of corticosteroids and hyaluronic acid directly into the hock joint. Corticosteroids help reduce inflammation, while hyaluronic acid provides lubrication and supports joint health. Joint injections can provide significant pain relief and improve the horse’s mobility, but the frequency of injections may vary depending on the individual horse and the severity of the condition.
- Regenerative Therapies: Regenerative therapies, such as platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and stem cell therapy, have gained popularity in the treatment of hock injuries. PRP involves injecting a concentrated solution of the horse’s own platelets, which contain growth factors, into the affected area to promote healing. Stem cell therapy utilizes the horse’s own stem cells, often derived from bone marrow or adipose tissue, to stimulate tissue repair and regeneration. These treatments have shown promising results in managing hock lameness and supporting the healing process.
- Surgical Interventions: In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to address certain hock injuries. Procedures such as arthroscopy, which involves the use of small incisions and a camera to visualize and treat joint problems, can be performed to remove bone fragments, smooth damaged cartilage, or address other specific issues. Surgical options are typically considered when conservative treatments have not been effective or in cases of severe injuries.
About SmartStride™ Ultra Pellets
Why SmartStride Ultra Pellets?
SmartStride™ Ultra Pellets represent the next generation of joint support for horses! In a 28-day research study at Texas A&M University, SmartStride Ultra was shown to support joint health including significantly increasing range of motion of the hock at the walk and a tendency to increase range of motion in the hock at the trot.
This unique formula was designed to provide your horse with cutting-edge ingredients for healthy joints, bones, tendons, and ligaments.
This formula includes:
- Researched support for hock health!
- Revolutionary and new ingredients including turmeric and resveratrol for supporting a normal response to inflammation and boron for maintaining bone health
- Tried and true ingredients such as glucosamine, chondroitin sulfate, and HA for joint health
- Collagen and silica for resilient tendons and ligaments
- A tasty pellet with no added sugar!
Whether your horse is in heavy work, or you’re just looking to make sure they have comprehensive support, joint supplements in this category are a great way to help maintain joint health. Click to learn more.